Getting started
You can store your audience’s language preferences as an attribute, and then use that attribute to send people messages in their preferred language!
How it works
When you add or update people, you can set an attributeA key-value pair that you associate with a person or an object—like a person’s name, the date they were created in your workspace, or a company’s billing date etc. Use attributes to target people and personalize messages. Attributes are analogous to traits in Data Pipelines. containing their language preference. Then, when you set up messages, you can click Add language to add one or more languages. You’ll set up your Default message, and then add content for each language.
When you send your message, people whose language attribute matches one of your message’s languages will receive the appropriate localization. Everybody else receives the Default message.
attribute] --> B[Set up
multi-language message] B --> C[Send
message] C --> D{Does a person's language
attribute match a message?} D -->|no| H[Person gets
default message] D -->|yes, lang=es| E[Person gets
Spanish message] D -->|yes, lang=fr| F[Person gets
French message] D -->|yes, lang=de| G[Person gets
German message]
Multi-language support
| Campaign/Message Type | SMS | Push | In-App | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campaigns | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Newsletters | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Broadcasts | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Transactional Messages | ✅ | ✅ |
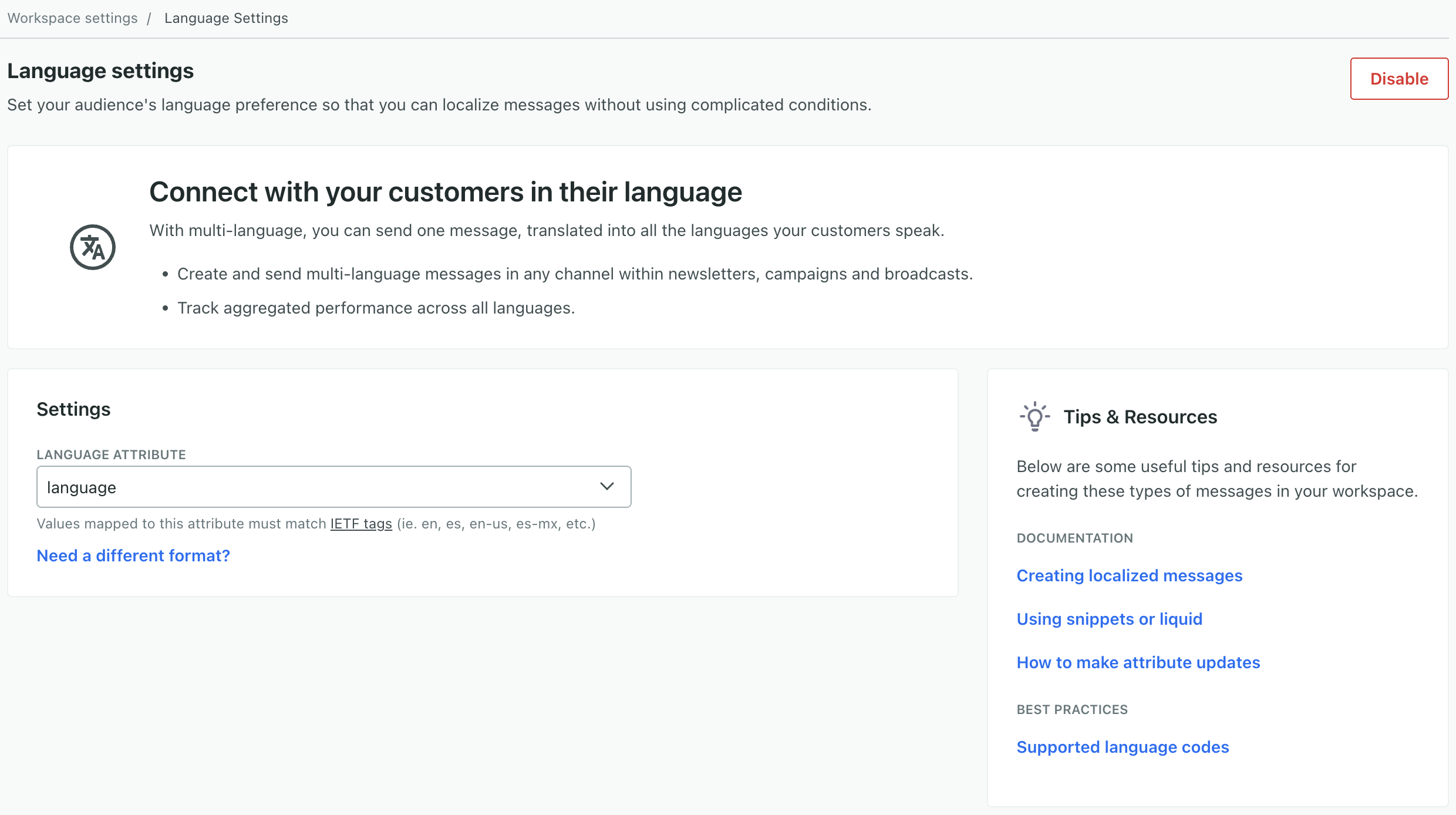
1. Set your language attribute
Before you can send localized messages, you need to go to Workspace Settings > Language settings and tell us what attributeA key-value pair that you associate with a person or an object—like a person’s name, the date they were created in your workspace, or a company’s billing date etc. Use attributes to target people and personalize messages. Attributes are analogous to traits in Data Pipelines. stores your audience’s language preferences. This attribute must store values we support, meaning they’re either:
- a two letter language code, like
enfor English - a four-letter language and region code, separated by a dash, like
en-USfor English speakers in the United States.

Go to Set up your localization attribute for more info.
2. Set up a multi-language message
When you create a message with multiple languages, you should always begin by drafting your Default message. This is the message intended for anybody who doesn’t match another language and should represent your “template” for other languages.
If you plan to send email content to a translation vendor, you’ll want to set up and export your Default message first, and then add languages when you receive them. Check out our best practices for help exporting email messages for your translation vendor and the quickest way to add your multi-language content.
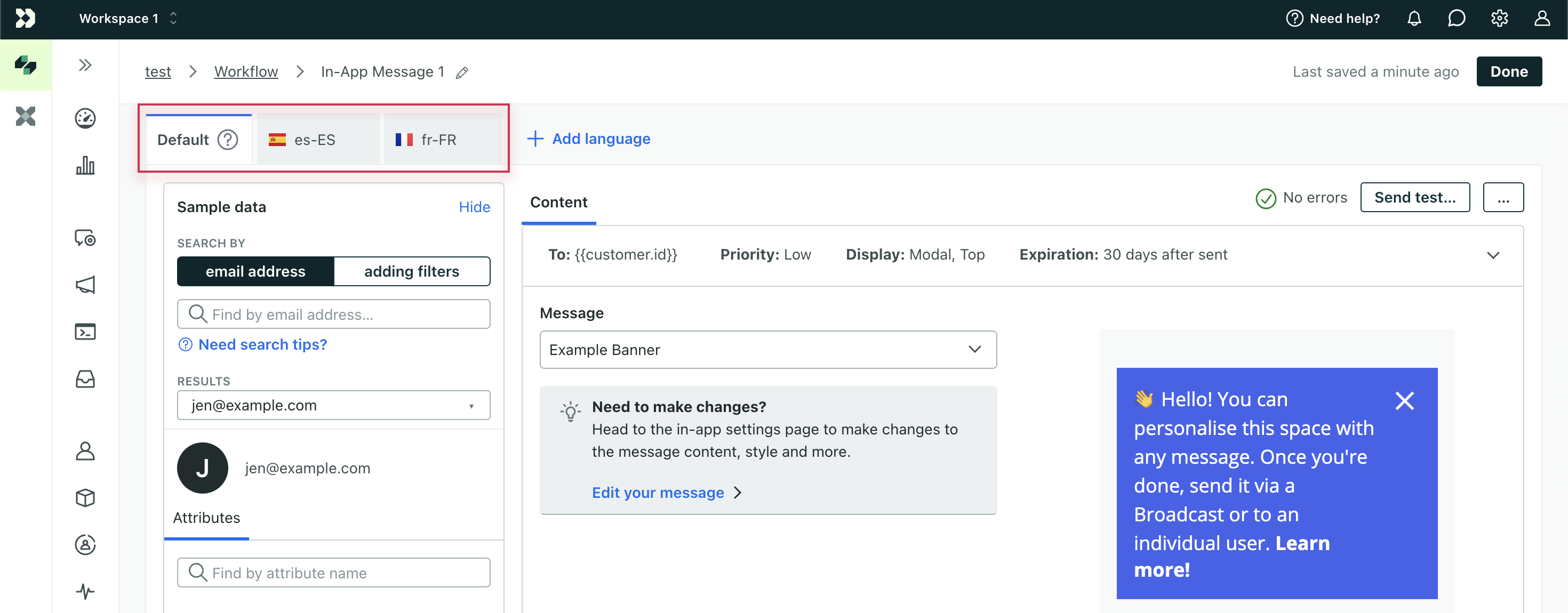
- Drag a message into your workflow then click it to view settings on the left.
- Set a Name for your message, and click Add Content.
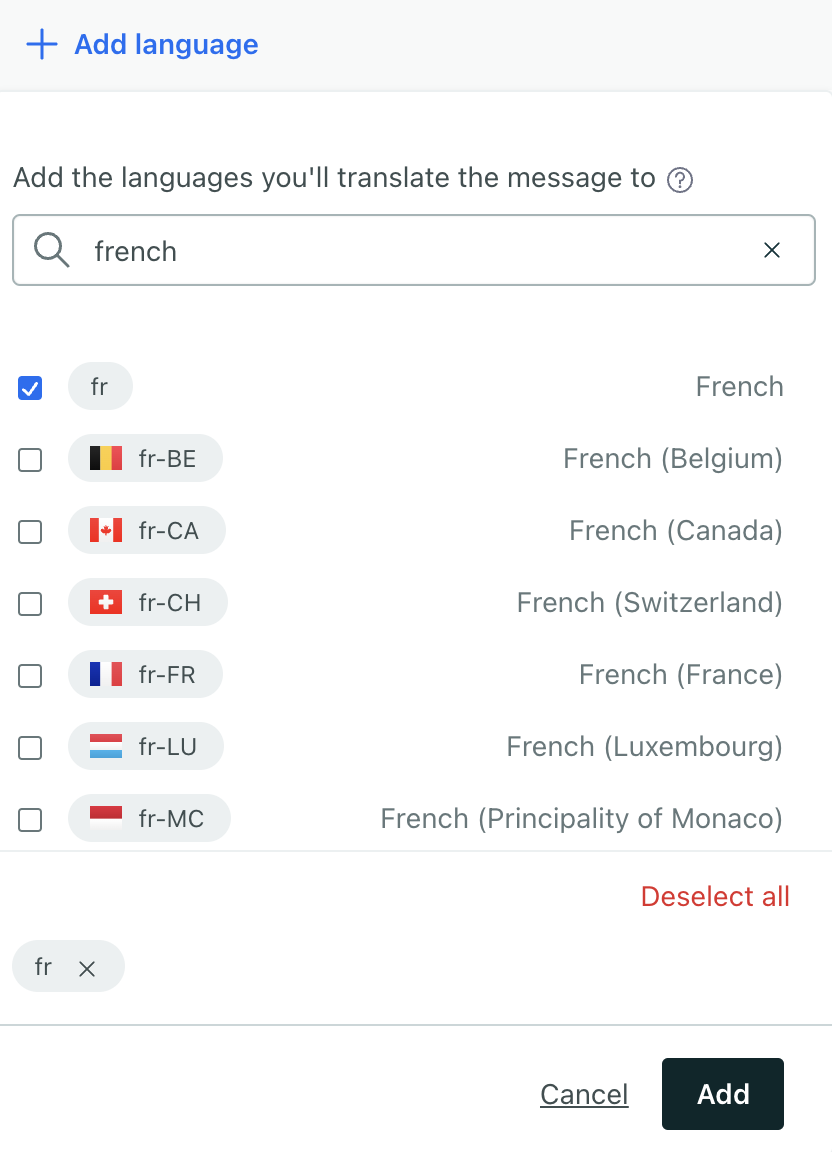
- Click Add language then check the languages you want. Click Add.

- Draft your Default message. This message should act as a “template” for your other languages. It will be the fallback if your customers do not have a language attribute.
- Add your content for each language. Use the tabs at the top of the message to switch between languages.

- When you’re done, save your changes.
Best practices
Export email to HTML for vendors
When you set up a message with multiple languages, you may need to send content to a translation vendor. To simplify this process, we suggest that you draft, test, and finalize your Default message first.
We recommend you export emails to HTML before you send them to a translation vendor:
- If you created your email with the drag and drop editor, click Actions > Export to HTML.
- If you created your email with the rich text editor, click HTML underneath the email header to copy/paste the source code.
- If you used the code editor, you can copy your email out to a separate file.
Make sure your translation vendor handles raw HTML
While we suggest you export custom HTML, make sure that your translation team can translate raw HTML before you export your email or switch editors. Remember, when you switch editor types, you cannot switch back.
Add translations for email from vendors
When you receive your translations from your translator(s):
- If you exported your HTML originally, copy/paste the translated HTML back to the rich text (click HTML first) or code editors. If you used the rich text editor, you may need to reformat text after pasting.
- If you didn’t export your HTML, or you used the drag and drop editor, paste localized text back into the blocks of your message.
message] -.->F{Test message} A -.-> |Convert without testing| C[Convert to
Custom HTML] C --> D[Export and
send to translator] D -->|Get translations
back| E[Add languages] E --> G[Send message] F-.-> |Tests pass|C F-.-> |Tests fail|A
Consider liquid values
You might use liquidA syntax that supports variables, letting you personalize messages for your audience. For example, if you want to reference a person’s first name, you might use the variable {{customer.first_name}}. to personalize your message for your audience. Liquid doesn’t account for translations; we use the values stored on people’s profiles. Therefore, you’ll want to store values in native languages or use a set of static values.
If using static values, request your vendor translate these, too. Then you can use if statements to set specific, translated values depending on your audience’s language attribute.
{% if customer.language == 'fr' %}
Bonjour
{% elsif customer.language == 'es' %}
Hola
{% else %}
Hello // Default value
{% endif %}
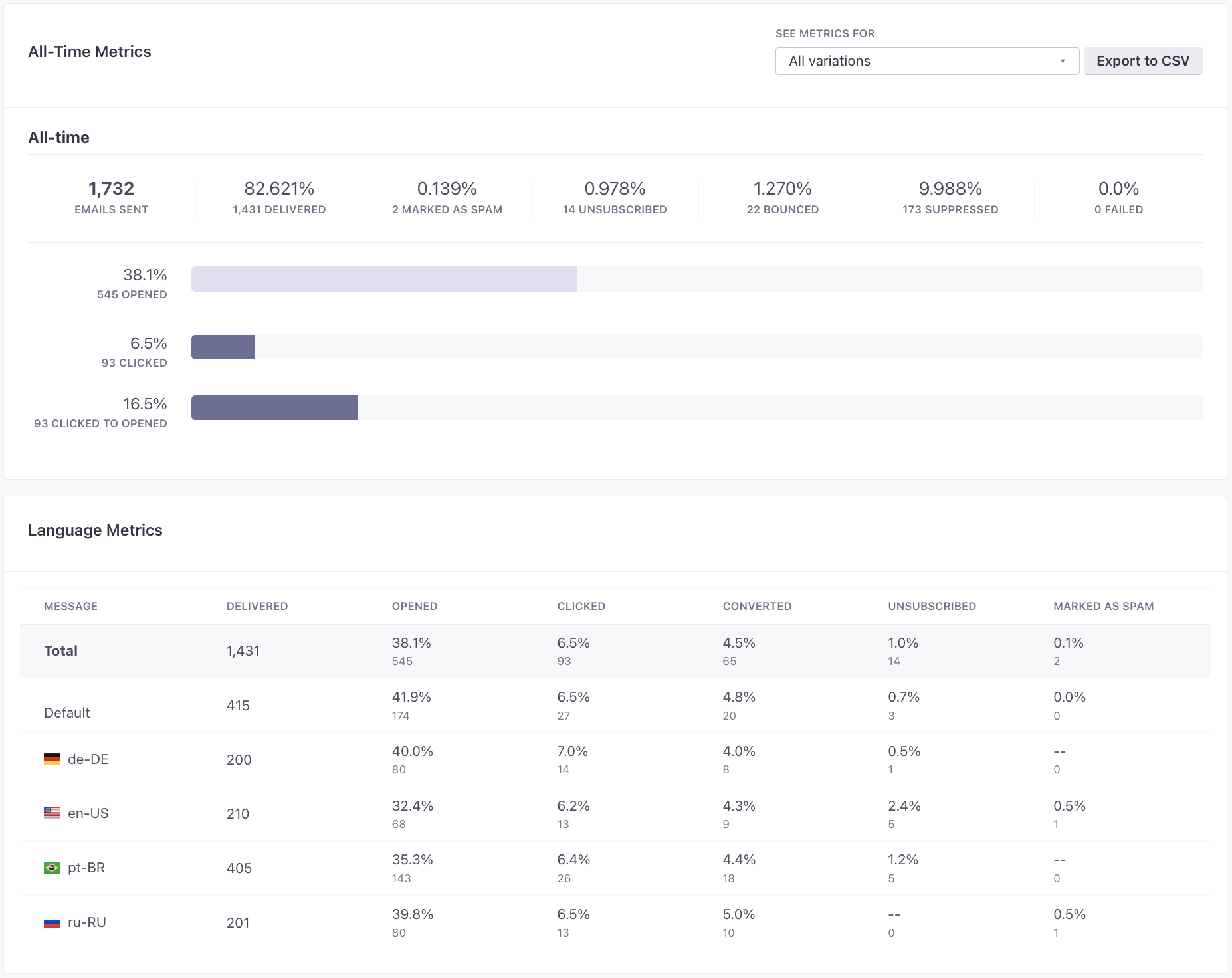
Multi-language metrics
When you send a message with multiple languages, we show metrics for each language. These metrics can help you make sure that your messages perform well in all of your audience’s languages.

Supported languages and locales
You must format the values of your language attribute as two-letter language codes with an optional two-letter region code separated by a dash, like en or en-US.
Language attributes are not case sensitive, but language-region codes must be separated by a dash. For example, both es-MX and es-mx represent Spanish formatted for speakers in Mexico.
These codes come from the ISO-3166-1 (alpha 2) and IETF standards respectively. If you’re looking for a language or locale that we don’t support, let us know!
| Language/Locale | Code |
| Afrikaans | af |
| Afrikaans (South Africa) | af-ZA |
| Amharic (Ethiopia) | am-ET |
| Arabic | ar |
| Arabic (U.A.E.) | ar-AE |
| Arabic (Bahrain) | ar-BH |
| Arabic (Algeria) | ar-DZ |
| Arabic (Egypt) | ar-EG |
| Arabic (Iraq) | ar-IQ |
| Arabic (Jordan) | ar-JO |
| Arabic (Kuwait) | ar-KW |
| Arabic (Lebanon) | ar-LB |
| Arabic (Libya) | ar-LY |
| Arabic (Morocco) | ar-MA |
| Arabic (Oman) | ar-OM |
| Arabic (Qatar) | ar-QA |
| Arabic (Saudi Arabia) | ar-SA |
| Arabic (Syria) | ar-SY |
| Arabic (Tunisia) | ar-TN |
| Arabic (Yemen) | ar-YE |
| Mapudungun (Chile) | arn-CL |
| Assamese (India) | as-IN |
| Azeri | az |
| Azeri (Cyrillic) (Azerbaijan) | az-Cyrl-AZ |
| Azeri (Latin) (Azerbaijan) | az-Latn-AZ |
| Bashkir (Russia) | ba-RU |
| Belarusian | be |
| Belarusian (Belarus) | be-BY |
| Bulgarian | bg |
| Bulgarian (Bulgaria) | bg-BG |
| Bengali (Bangladesh) | bn-BD |
| Bengali (India) | bn-IN |
| Tibetan (People's Republic of China) | bo-CN |
| Breton (France) | br-FR |
| Bosnian (Cyrillic) (Bosnia and Herzegovina) | bs-Cyrl-BA |
| Bosnian (Latin) (Bosnia and Herzegovina) | bs-Latn-BA |
| Catalan | ca |
| Catalan (Catalan) | ca-ES |
| Corsican (France) | co-FR |
| Czech | cs |
| Czech (Czech Republic) | cs-CZ |
| Welsh (United Kingdom) | cy-GB |
| Danish | da |
| Danish (Denmark) | da-DK |
| German | de |
| German (Austria) | de-AT |
| German (Switzerland) | de-CH |
| German (Germany) | de-DE |
| German (Liechtenstein) | de-LI |
| German (Luxembourg) | de-LU |
| Lower Sorbian (Germany) | dsb-DE |
| Divehi | dv |
| Divehi (Maldives) | dv-MV |
| Greek | el |
| Greek (Greece) | el-GR |
| English | en |
| English (Caribbean) | en-029 |
| English (Australia) | en-AU |
| English (Belize) | en-BZ |
| English (Canada) | en-CA |
| English (United Kingdom) | en-GB |
| English (Ireland) | en-IE |
| English (India) | en-IN |
| English (Jamaica) | en-JM |
| English (Malaysia) | en-MY |
| English (New Zealand) | en-NZ |
| English (Republic of the Philippines) | en-PH |
| English (Singapore) | en-SG |
| English (Trinidad and Tobago) | en-TT |
| English (United States) | en-US |
| English (South Africa) | en-ZA |
| English (Zimbabwe) | en-ZW |
| Spanish | es |
| Spanish (Argentina) | es-AR |
| Spanish (Bolivia) | es-BO |
| Spanish (Chile) | es-CL |
| Spanish (Colombia) | es-CO |
| Spanish (Costa Rica) | es-CR |
| Spanish (Dominican Republic) | es-DO |
| Spanish (Ecuador) | es-EC |
| Spanish (Spain) | es-ES |
| Spanish (Guatemala) | es-GT |
| Spanish (Honduras) | es-HN |
| Spanish (Latin America) | es-LA |
| Spanish (Mexico) | es-MX |
| Spanish (Nicaragua) | es-NI |
| Spanish (Panama) | es-PA |
| Spanish (Peru) | es-PE |
| Spanish (Puerto Rico) | es-PR |
| Spanish (Paraguay) | es-PY |
| Spanish (El Salvador) | es-SV |
| Spanish (United States) | es-US |
| Spanish (Uruguay) | es-UY |
| Spanish (Venezuela) | es-VE |
| Estonian | et |
| Estonian (Estonia) | et-EE |
| Basque | eu |
| Basque (Basque) | eu-ES |
| Persian | fa |
| Persian (Iran) | fa-IR |
| Finnish | fi |
| Finnish (Finland) | fi-FI |
| Filipino (Philippines) | fil-PH |
| Faroese | fo |
| Faroese (Faroe Islands) | fo-FO |
| French | fr |
| French (Belgium) | fr-BE |
| French (Canada) | fr-CA |
| French (Switzerland) | fr-CH |
| French (France) | fr-FR |
| French (Luxembourg) | fr-LU |
| French (Principality of Monaco) | fr-MC |
| Frisian (Netherlands) | fy-NL |
| Irish (Ireland) | ga-IE |
| Scottish Gaelic (United Kingdom) | gd-GB |
| Galician | gl |
| Galician (Galician) | gl-ES |
| Alsatian (France) | gsw-FR |
| Gujarati | gu |
| Gujarati (India) | gu-IN |
| Hausa (Latin) (Nigeria) | ha-Latn-NG |
| Hebrew | he |
| Hebrew (Israel) | he-IL |
| Hindi | hi |
| Hindi (India) | hi-IN |
| Croatian | hr |
| Croatian (Latin) (Bosnia and Herzegovina) | hr-BA |
| Croatian (Croatia) | hr-HR |
| Upper Sorbian (Germany) | hsb-DE |
| Hungarian | hu |
| Hungarian (Hungary) | hu-HU |
| Armenian | hy |
| Armenian (Armenia) | hy-AM |
| Indonesian | id |
| Indonesian (Indonesia) | id-ID |
| Igbo (Nigeria) | ig-NG |
| Yi (People's Republic of China) | ii-CN |
| Icelandic | is |
| Icelandic (Iceland) | is-IS |
| Italian | it |
| Italian (Switzerland) | it-CH |
| Italian (Italy) | it-IT |
| Inuktitut (Syllabics) (Canada) | iu-Cans-CA |
| Inuktitut (Latin) (Canada) | iu-Latn-CA |
| Japanese | ja |
| Japanese (Japan) | ja-JP |
| Georgian | ka |
| Georgian (Georgia) | ka-GE |
| Kazakh | kk |
| Kazakh (Kazakhstan) | kk-KZ |
| Greenlandic (Greenland) | kl-GL |
| Khmer (Cambodia) | km-KH |
| Kannada | kn |
| Kannada (India) | kn-IN |
| Korean | ko |
| Korean (Korea) | ko-KR |
| Konkani | kok |
| Konkani (India) | kok-IN |
| Kyrgyz | ky |
| Kyrgyz (Kyrgyzstan) | ky-KG |
| Latin | la |
| Luxembourgish (Luxembourg) | lb-LU |
| Lao (Lao P.D.R.) | lo-LA |
| Lithuanian | lt |
| Lithuanian (Lithuania) | lt-LT |
| Latvian | lv |
| Latvian (Latvia) | lv-LV |
| Maori (New Zealand) | mi-NZ |
| Macedonian | mk |
| Macedonian (Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia) | mk-MK |
| Malayalam (India) | ml-IN |
| Mongolian | mn |
| Mongolian (Cyrillic) (Mongolia) | mn-MN |
| Mongolian (Traditional Mongolian) (People's Republic of China) | mn-Mong-CN |
| Mohawk (Canada) | moh-CA |
| Marathi | mr |
| Marathi (India) | mr-IN |
| Malay | ms |
| Malay (Brunei Darussalam) | ms-BN |
| Malay (Malaysia) | ms-MY |
| Maltese (Malta) | mt-MT |
| "Norwegian (Bokmål)" | nb |
| "Norwegian, Bokmål (Norway)" | nb-NO |
| Nepali (Nepal) | ne-NP |
| Dutch | nl |
| Dutch (Belgium) | nl-BE |
| Dutch (Netherlands) | nl-NL |
| "Norwegian, Nynorsk (Norway)" | nn-NO |
| Norwegian | no |
| Sesotho sa Leboa (South Africa) | nso-ZA |
| Occitan (France) | oc-FR |
| Oriya (India) | or-IN |
| Punjabi | pa |
| Punjabi (India) | pa-IN |
| Polish | pl |
| Polish (Poland) | pl-PL |
| Dari (Afghanistan) | prs-AF |
| Pashto (Afghanistan) | ps-AF |
| Portuguese | pt |
| Portuguese (Brazil) | pt-BR |
| Portuguese (Portugal) | pt-PT |
| K'iche (Guatemala) | qut-GT |
| Quechua (Bolivia) | quz-BO |
| Quechua (Ecuador) | quz-EC |
| Quechua (Peru) | quz-PE |
| Romansh (Switzerland) | rm-CH |
| Romanian | ro |
| Romanian (Romania) | ro-RO |
| Russian | ru |
| Russian (Russia) | ru-RU |
| Kinyarwanda (Rwanda) | rw-RW |
| Sanskrit | sa |
| Sanskrit (India) | sa-IN |
| Yakut (Russia) | sah-RU |
| Sami (Northern) | se |
| Sami (Northern) (Finland) | se-FI |
| Sami (Northern) (Norway) | se-NO |
| Sami (Northern) (Sweden) | se-SE |
| Sinhala (Sri Lanka) | si-LK |
| Slovak | sk |
| Slovak (Slovakia) | sk-SK |
| Slovenian | sl |
| Slovenian (Slovenia) | sl-SI |
| Sami (Southern) (Norway) | sma-NO |
| Sami (Southern) (Sweden) | sma-SE |
| Sami (Lule) (Norway) | smj-NO |
| Sami (Lule) (Sweden) | smj-SE |
| Sami (Inari) (Finland) | smn-FI |
| Sami (Skolt) (Finland) | sms-FI |
| Somali | so |
| Somali (Djibouti) | so-DJ |
| Somali (Ethiopia) | so-ET |
| Somali (Kenya) | so-KE |
| Somali (Somalia) | so-SO |
| Albanian | sq |
| Albanian (Albania) | sq-AL |
| Serbian | sr |
| Serbian (Cyrillic) (Bosnia and Herzegovina) | sr-Cyrl-BA |
| Serbian (Cyrillic) (Serbia and Montenegro (Former)) | sr-Cyrl-CS |
| Serbian (Cyrillic) (Montenegro) | sr-Cyrl-ME |
| Serbian (Cyrillic) (Serbia) | sr-Cyrl-RS |
| Serbian (Latin) (Bosnia and Herzegovina) | sr-Latn-BA |
| Serbian (Latin) (Serbia and Montenegro (Former)) | sr-Latn-CS |
| Serbian (Latin) (Montenegro) | sr-Latn-ME |
| Serbian (Latin) (Serbia) | sr-Latn-RS |
| Swedish | sv |
| Swedish (Finland) | sv-FI |
| Swedish (Sweden) | sv-SE |
| Kiswahili | sw |
| Kiswahili (Kenya) | sw-KE |
| Syriac | syr |
| Syriac (Syria) | syr-SY |
| Tamil | ta |
| Tamil (India) | ta-IN |
| Telugu | te |
| Telugu (India) | te-IN |
| Tajik (Cyrillic) (Tajikistan) | tg-Cyrl-TJ |
| Thai | th |
| Thai (Thailand) | th-TH |
| Turkmen (Turkmenistan) | tk-TM |
| Setswana (South Africa) | tn-ZA |
| Turkish | tr |
| Turkish (Turkey) | tr-TR |
| Tatar | tt |
| Tatar (Russia) | tt-RU |
| Tamazight (Latin) (Algeria) | tzm-Latn-DZ |
| Uyghur (People's Republic of China) | ug-CN |
| Ukrainian | uk |
| Ukrainian (Ukraine) | uk-UA |
| Urdu | ur |
| Urdu (Islamic Republic of Pakistan) | ur-PK |
| Uzbek | uz |
| Uzbek (Cyrillic) (Uzbekistan) | uz-Cyrl-UZ |
| Uzbek (Latin) (Uzbekistan) | uz-Latn-UZ |
| Vietnamese | vi |
| Vietnamese (Vietnam) | vi-VN |
| Wolof (Senegal) | wo-SN |
| isiXhosa (South Africa) | xh-ZA |
| Yoruba (Nigeria) | yo-NG |
| Chinese (Simplified) | zh-Hans |
| Chinese (Traditional) | zh-Hant |
| Chinese (People's Republic of China) | zh-CN |
| Chinese (Hong Kong S.A.R.) | zh-HK |
| Chinese (Macao S.A.R.) | zh-MO |
| Chinese (Singapore) | zh-SG |
| Chinese (Taiwan) | zh-TW |
| isiZulu (South Africa) | zu-ZA |

